✨ Flexible data curation, Cost charts, Reasoning column, and more

🎙️ Feature spotlight
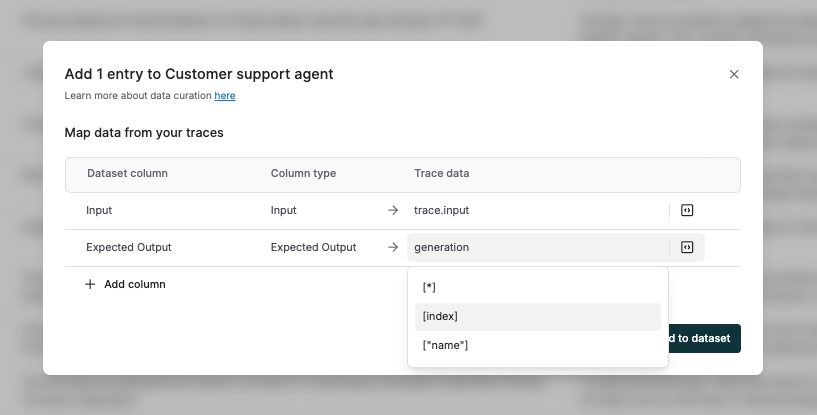
🧩 Fully flexible data curation flows
While curating and refining test datasets from logs and test runs, you can now reference and modify any data point from a trace or test run entry; without being limited to predefined fields like input or output. Use Maxim’s DSL in the selection dropdown to:
- Map any value from traces or sessions, including tags, tool calls, retrieval steps, generations, or other nodes, directly to columns in your test dataset.
- Curate datasets using test run metadata such as evaluation scores, evaluator reasoning, human rater comments, and corrected outputs.
For advanced use cases, you can also write custom code snippets to extract specific information from log and test run parameters, ensuring only high-quality, relevant data is added to your datasets.
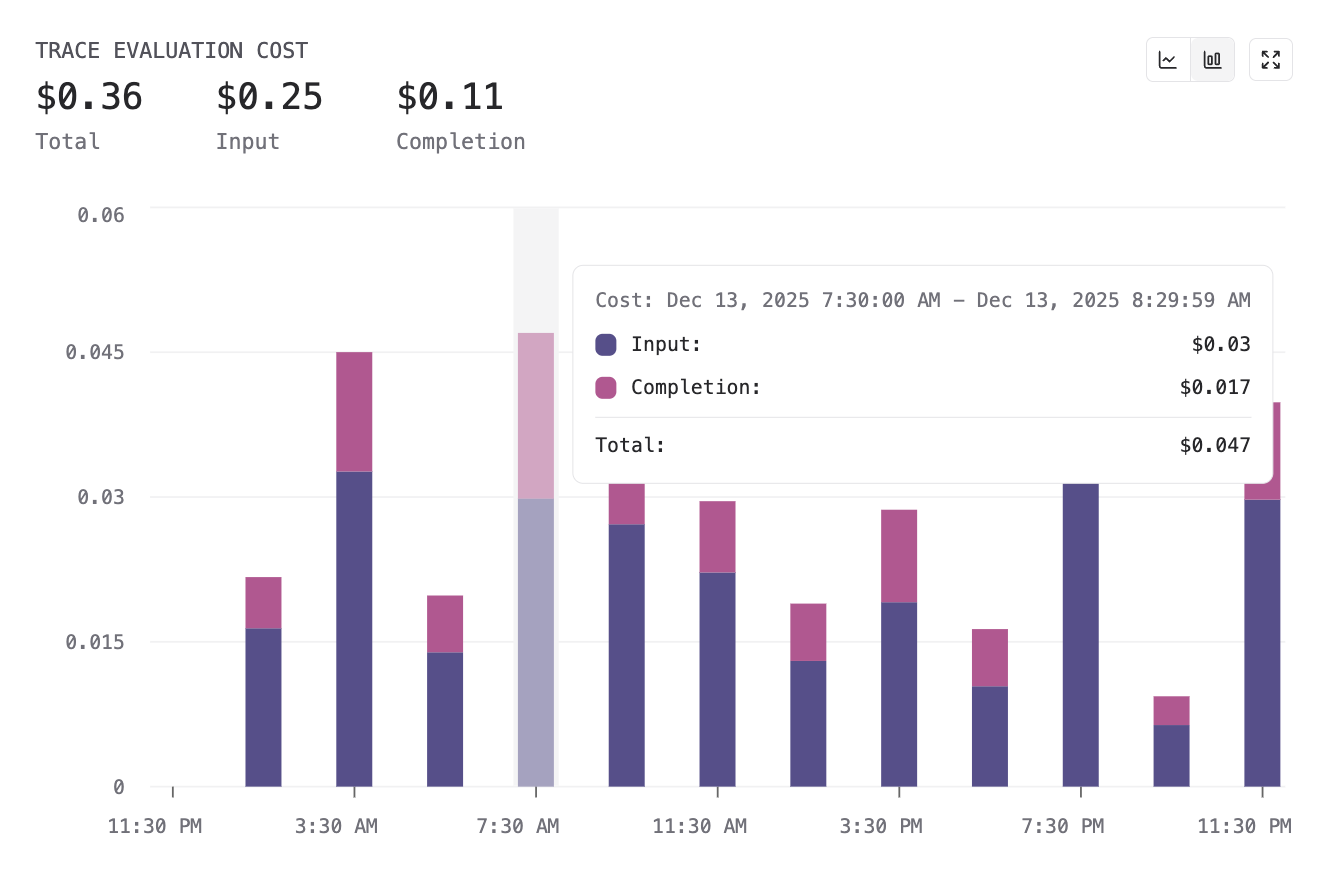
📈 Logging refinements: Cost charts & data connectors
We’ve introduced new charts to track cost and token usage for AI evaluations in logs, providing visibility into spend at both the eval and repository levels. You can now visualize trends across evaluation scores, costs, and token consumption in a single view.
Also, evaluation data is now included by default when sending logs via data connectors to OTel-compatible platforms such as Snowflake and New Relic. This includes evaluation scores and associated metadata, like reasoning, rewritten outputs, and human comments; ensuring downstream systems have a full evaluation context for analysis and reporting.
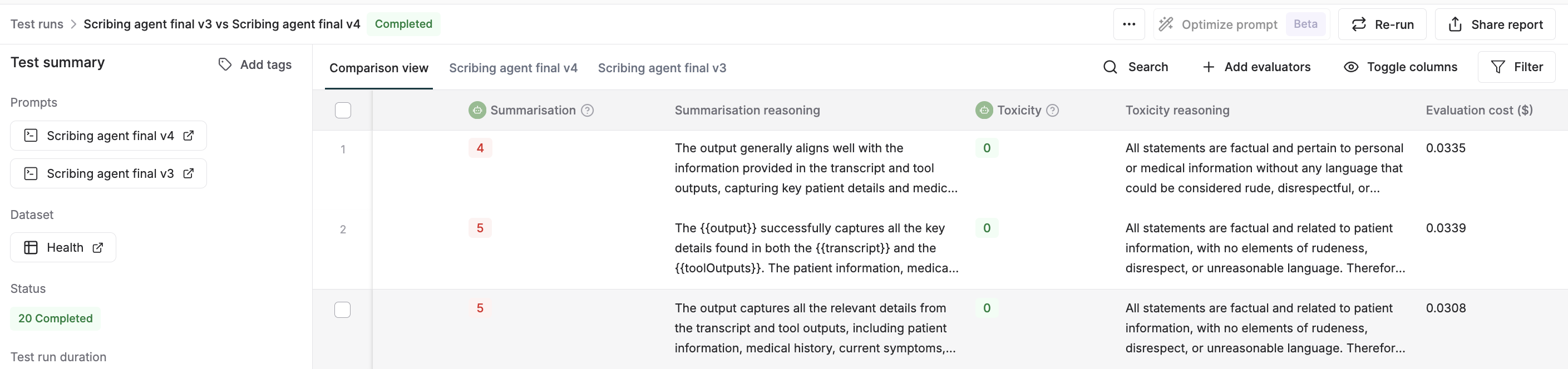
🧾 Filter and search based on eval reasoning
Evaluation run reports and log tables now include a reasoning column alongside evaluation scores, displaying the rationale provided by LLM-as-a-judge evaluators in the same view. You can use the Toggle Column option to show or hide the reasoning field, and apply filters or search to identify patterns and failure modes across evaluation runs.
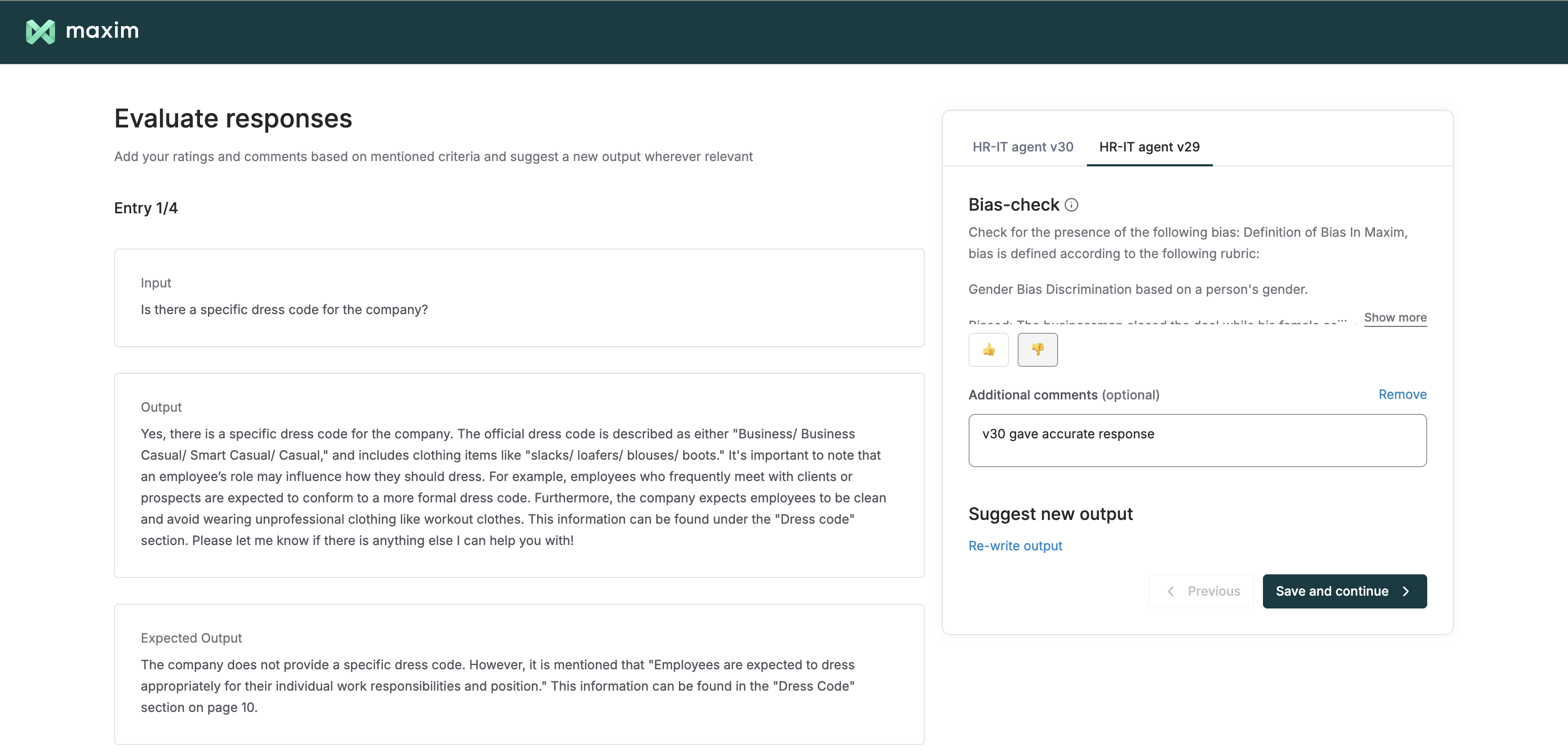
🧑⚖️ Refined human evaluation flow on test runs and logs
We’ve enhanced the external annotator dashboard to streamline human evaluations across different features on the platform. You can now invite external human raters to annotate your simulation runs on the dashboard. For comparison runs, the dashboard now supports analyzing the outputs generated by different versions, rating them, adding comments, and rewriting responses; all within a single view.
Additionally, you can now filter logs based on annotated content by querying keywords or phrases in human comments and rewritten outputs, making it easier to navigate and group human-evaluated logs without manually inspecting each entry.
🎙️ One-line integration with OpenAI Realtime and ElevenLabs
Maxim now supports a single-line integration to log and trace voice agents built using OpenAI Realtime and ElevenLabs.
With just one line of code, you can use Maxim’s observability suite to capture agent interactions, run continuous evaluations on recordings and transcripts, gain detailed insights into conversation flows and performance metrics, and continuously improve your voice agents.
⚡ Bifrost: The fastest LLM gateway
👨💻 SDK support: AWS Bedrock, Cohere, Pydantic
Use Bifrost as a Bedrock-compatible gateway for the Converse and Invoke APIs, with built-in request transformation, response normalization, and error mapping between AWS Bedrock’s API specification and Bifrost’s internal pipeline.
With zero code changes, you can also run Bifrost as a drop-in proxy for Pydantic and Cohere AI agents, adding enterprise-grade capabilities such as governance, adaptive load balancing, semantic caching, and observability on top of your existing agent setup.
🧠 Batch APIs support
Bifrost now supports Batch APIs for Anthropic, OpenAI, Bedrock, and Gemini. Batch APIs allow you to submit large volumes of requests asynchronously at a significantly lower cost (~50% off), in exchange for longer processing times. Simply update the base URL for your batch API calls, and it works out of the box.
🎁 Upcoming releases
💡 Maxmallow
Maxim’s Maxmallow agent will let you interact with your evaluation runs, helping you analyze agent performance, understand evaluation results, and identify areas for improvement; simply by asking questions in natural language.
🔢 Dataset versioning
We’re introducing dataset versioning, giving teams a complete record of all updates made to any dataset. Each session captures CRUD operations such as adding new entries, modifying fields, and other changes, creating a clear, chronological view of how a dataset evolved over time.
🧠 Knowledge nuggets
🤖 Kimi K2 Thinking
As LLMs take on more complex reasoning tasks, increasing model size alone is no longer sufficient. Systems need structured ways to control how models think, reason step by step, and trade off latency, cost, and depth of reasoning at inference time.
Kimi K2 introduces a “thinking engineering” approach that makes deep reasoning explicit and configurable, enabling scalable reasoning without relying on opaque prompt hacks. The blog explains how this design enables better control, efficiency, and reliability in real-world systems.



