Integrating Zed Editor with Bifrost Gateway
Akshay Deo
Dec 02, 2025 · 5 min read

Zed is a high-performance, collaborative code editor built for the modern development workflow. With native AI assistant integration, Zed can leverage language models directly within the editor for code generation, refactoring, and explanation. Integrating Zed with Bifrost Gateway unlocks multi-provider model access, MCP tools, and observability - transforming Zed's AI assistant into a flexible, enterprise-ready coding companion.
Architecture Overview
Zed's language model integration supports OpenAI-compatible providers, making it naturally compatible with Bifrost. The architecture:
- Zed's AI assistant sends requests to configured language model providers
- Bifrost receives requests at its OpenAI-compatible endpoint (
/openai) - Bifrost routes to the configured provider based on the selected model
- Provider responses are translated to OpenAI format
- Zed receives responses and renders them inline in the editor
This allows Zed users to access multiple models - Claude, GPT-4, Gemini, or others - without leaving the editor, while Bifrost handles provider complexity, authentication, and tool integration.
Setup
Step 1: Configure Bifrost Provider
Add the Bifrost configuration to Zed's settings. Open settings via Cmd+, (Mac) or Ctrl+, (Linux/Windows), then navigate to the language models section:
Step 2: Reload Workspace
After saving the configuration, reload the Zed workspace to ensure the editor recognizes the new provider:
- Mac:
Cmd+Shift+P→ "Reload Window" - Linux/Windows:
Ctrl+Shift+P→ "Reload Window"
Alternatively, restart Zed completely. The Bifrost provider should now appear in the model selector.
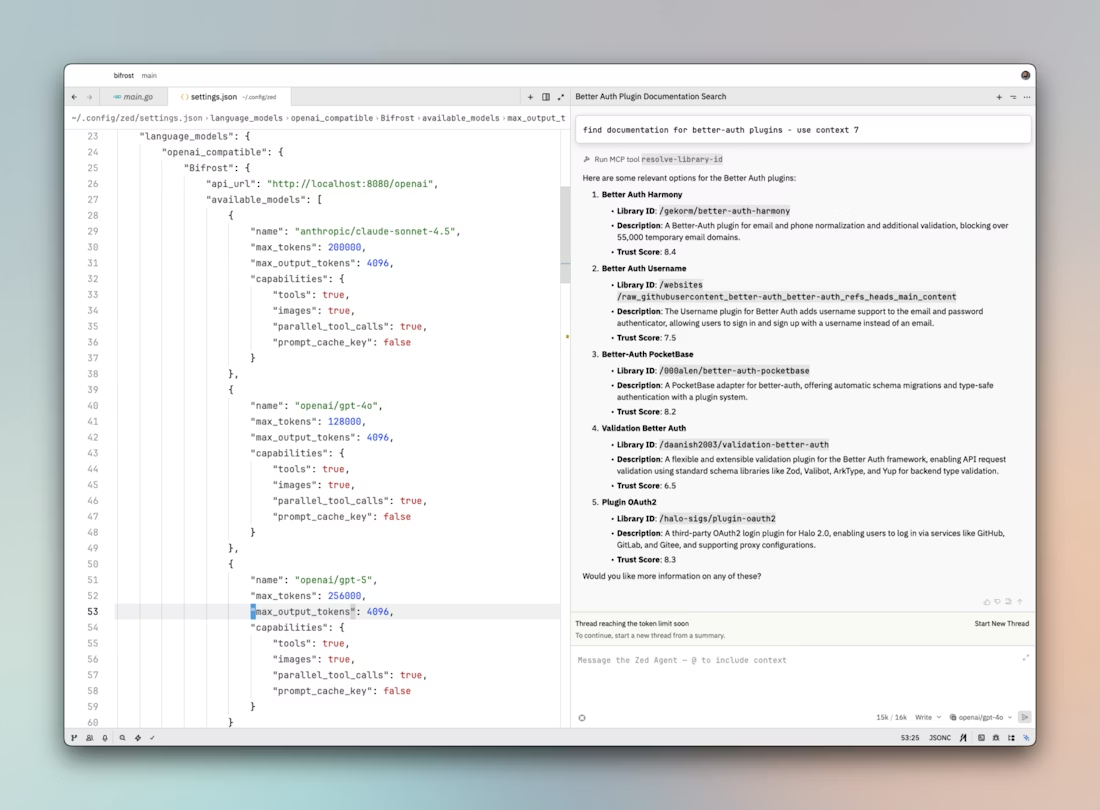
Configuration Breakdown
api_url
The endpoint where Zed sends language model requests. Replace {{bifrost-base-url}} with your actual Bifrost deployment.
The /openai path tells Bifrost to use its OpenAI-compatible handler, translating all requests and responses to/from OpenAI's format.
available_models
An array defining which models Zed can access through Bifrost. Each model requires:
name: The provider/model identifier in Bifrost's format (provider/model). Must match a model configured in Bifrost. Examples:
anthropic/claude-sonnet-4.5openai/gpt-4ogoogle/gemini-2.0-flash-exp
max_tokens: The model's total context window size. This is the combined input + output token limit:
- Claude Sonnet 4.5: 200,000 tokens
- GPT-4o: 128,000 tokens
- GPT-5: 256,000 tokens (example)
max_output_tokens: Maximum tokens the model can generate in a single response. Typically 4,096 for most models, though some support more (Claude supports up to 8,192).
capabilities: Feature flags that tell Zed what the model supports:
tools: true- Model can use function/tool calling. Essential for MCP integration.images: true- Model can process images. Useful for screenshot-based debugging or UI work.parallel_tool_calls: true- Model can invoke multiple tools simultaneously, improving efficiency.prompt_cache_key: false- Whether the model supports prompt caching. Set totruefor Claude models with caching enabled in Bifrost.
Key Capabilities
Multi-Model Access Within Editor
With Bifrost, Zed's AI assistant can access any configured model. Users switch models via Zed's model selector without reconfiguring:
Claude Sonnet 4.5: Best for complex refactoring, architectural decisions, and nuanced code understanding. Use for high-stakes changes.
GPT-4o: Balanced performance for general coding tasks. Excellent for explanations and quick generations.
GPT-5: Cutting-edge capabilities (when available). Useful for experimental features or maximum performance.
Other Providers: Add Gemini, local models, or proprietary models to the configuration. Zed treats them identically.
This flexibility allows developers to choose the right model for each task—powerful models for complexity, fast models for simple queries—without leaving the editor.
Inline Code Generation and Editing
Zed's AI assistant works directly in the editor buffer:
Generate from Context: Highlight code, invoke the assistant, and describe changes. The model sees highlighted code as context and generates modifications inline.
Refactoring: Select a function, ask for refactoring, and Zed applies changes directly. With Bifrost's MCP tools, the model can read surrounding files for better context.
Code Explanation: Highlight unfamiliar code and ask for explanation. The assistant provides inline documentation without switching contexts.
Bug Fixing: Describe a bug, and the model suggests fixes with reasoning. Apply changes with a single keystroke.
MCP Tools Integration
When Bifrost has MCP tools configured, Zed's AI assistant automatically gains access:
Filesystem Access: The assistant can read files beyond what's currently open in the editor. For example, when generating test code, the model reads the implementation file even if it's not visible.
Project Structure Understanding: With filesystem tools, the model comprehends your entire project layout—module organization, configuration files, dependency management.
Database Schema: When writing database code, the model queries schema information via MCP to generate accurate SQL or ORM code.
Web Search: For tasks requiring current documentation or API changes, the model searches the web transparently. You see the final answer without manual searches.
Git Integration: The model can check current branch, recent commits, or file history to provide context-aware suggestions.
These tools enhance Zed's already powerful inline coding features with external context that makes suggestions more accurate and project-specific.
Real-Time Observability
All Zed AI assistant interactions flow through Bifrost and appear in the dashboard at http://localhost:8080/logs:
Request/Response Pairs: See exactly what Zed sent to the model and what came back. Useful for understanding how Zed constructs prompts from editor context.
Token Usage: Monitor consumption per request. Inline editing can be token-intensive with large context windows, so tracking helps manage costs.
Model Selection Patterns: Which models do you actually use most? Might inform which to prioritize or cache.
Error Tracking: When assistant requests fail, logs show whether it's rate limiting, model issues, or configuration problems.
Performance Metrics: Track response latency. Slow responses impact editing flow, so identifying bottlenecks (network, model, tools) helps optimization.
Collaborative Benefits
For teams using Zed's collaborative editing features, Bifrost provides shared benefits:
Consistent Model Access: All team members access the same models through shared Bifrost configuration, ensuring consistent code quality.
Centralized Cost Management: Instead of individual API keys, the team shares Bifrost's provider configuration. Administrators control costs centrally.
Unified Observability: Team leads see all AI assistant usage across the team, identifying patterns or issues affecting multiple developers.
Standardized Tools: MCP tools configured in Bifrost are available to everyone, ensuring consistent capabilities across the team.
Conclusion
Integrating Zed Editor with Bifrost Gateway transforms Zed's AI assistant into a flexible, enterprise-ready coding companion. Developers gain access to multiple models - switching seamlessly based on task requirements - while benefiting from MCP tool integration that provides real project context, not just guesses.
The configuration is straightforward - a single JSON block in settings - but the capabilities scale significantly. Teams achieve consistent model access, centralized cost management, and unified observability. Individual developers enjoy the freedom to choose optimal models for each task, backed by comprehensive tooling that makes suggestions more accurate and contextually aware.
For organizations investing in AI-assisted development, Bifrost provides the infrastructure layer that makes Zed's editor integration production-ready: model flexibility, observability, failover, cost control, and tool integration - all transparent to the coding experience.