Integrating LibreChat with Bifrost Gateway
Akshay Deo
Nov 14, 2025 · 6 min read

LibreChat is an open-source chat interface that provides a ChatGPT-like experience with support for multiple AI providers. Integrating it with Bifrost Gateway adds a layer of abstraction that enables unified model access, MCP tools, observability, and load balancing across different providers - all without modifying LibreChat's codebase.
Architecture Overview
LibreChat's custom endpoint feature allows integration with any OpenAI-compatible API. Bifrost leverages this by exposing an OpenAI-compatible endpoint that translates requests to any configured provider. The integration works as follows:
- LibreChat sends requests to Bifrost's
/v1endpoint using OpenAI's API format - Bifrost receives the request and routes it based on the configured provider/model
- Bifrost translates the request to the target provider's format (Anthropic, Google, etc.)
- The response flows back through Bifrost, where it's logged and translated back to OpenAI format
- LibreChat receives a standard OpenAI-formatted response
This architecture means LibreChat can access Claude, Gemini, or any other model through a unified interface, while Bifrost handles provider-specific details.
Installation Prerequisites
LibreChat Installation
LibreChat can be installed using Docker Compose or npm. Docker Compose is recommended as it bundles all dependencies:
Docker Compose (Recommended):
- Includes MongoDB for conversation storage
- Includes MeiliSearch for search functionality
- Includes rag_api and vectordb for file handling across endpoints
- Ensures consistent environment across deployments
- Simplifies dependency management
npm Installation:
- Requires manual MongoDB setup
- Requires manual MeiliSearch configuration
- Requires separate rag_api and vectordb setup
- More control but higher complexity
Configuration
Step 1: Configure librechat.yaml
Add Bifrost as a custom endpoint in your librechat.yaml file:
Configuration Breakdown
name: Display name for the endpoint in LibreChat's UI. Users will see "Bifrost" in the provider selector.
apiKey: Set to "dummy" when Bifrost doesn't require authentication. If you've enabled authentication in Bifrost, replace this with your actual API key.
baseURL: The endpoint where LibreChat sends requests. Three scenarios:
http://host.docker.internal:8080/v1- When LibreChat runs in Docker and Bifrost runs on the host machine. Docker'shost.docker.internalhostname resolves to the host's localhost.http://localhost:8080/v1- When both LibreChat and Bifrost run directly on the host (no containers).http://{bifrost-container-name}:8080/v1- When both run in the same Docker network. Replace{bifrost-container-name}with your actual container name.
models.default: Array of models available in the dropdown. Format is "provider/model". These must match models configured in your Bifrost instance.
models.fetch: When true, LibreChat attempts to fetch available models from Bifrost's /v1/models endpoint. This dynamically populates the model list rather than using hardcoded values.
titleConvo: Enables automatic conversation title generation. When true, LibreChat uses the specified titleModel to generate meaningful conversation titles from initial messages.
titleModel: Model used for generating conversation titles. Should be a fast, cost-effective model since this runs frequently.
summarize: Enables conversation summarization. Useful for long conversations that need condensing.
summaryModel: Model used for generating summaries. Can be the same as or different from titleModel.
forcePrompt: When true, forces LibreChat to send a system prompt on every request. Useful for enforcing specific behavior but increases token usage.
modelDisplayLabel: Label shown in the UI for models from this endpoint. Helps users identify they're using Bifrost-routed models.
iconURL: Custom icon displayed next to the provider name. Uses Bifrost's logo in the example.
Step 2: Docker-Specific Configuration
If running LibreChat in Docker, the librechat.yaml file isn't automatically loaded. You need to mount it into the container.
Create or edit docker-compose.override.yml:
This mounts your local librechat.yaml into the container at the expected path. See LibreChat's custom endpoints documentation for detailed instructions.
Step 3: Start LibreChat
After configuration:
LibreChat should now show "Bifrost" in the provider dropdown, with access to all configured models.
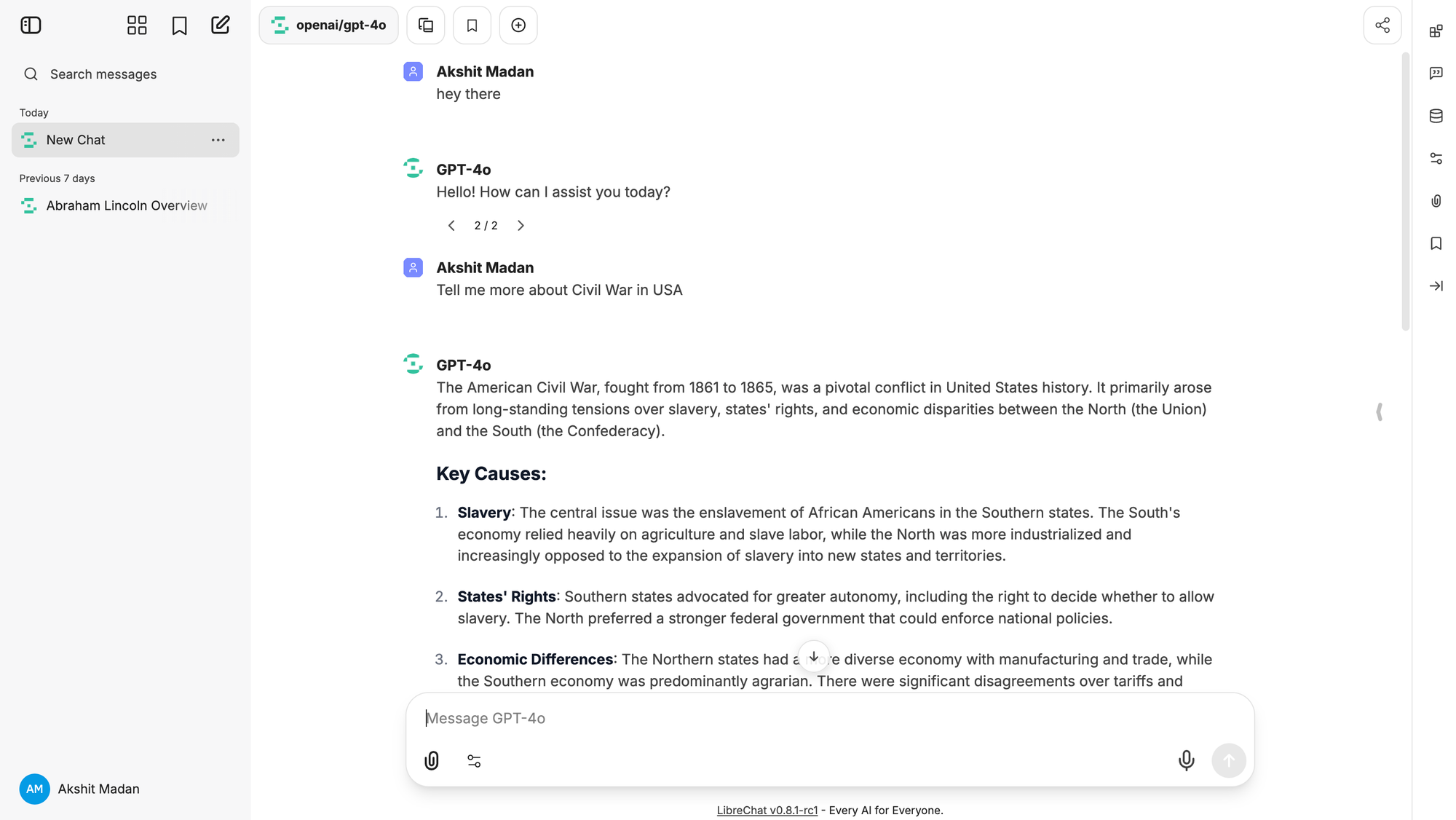
Key Features
Unified Model Access
Through Bifrost, LibreChat can access models from multiple providers using a single configuration. Users select models like:
openai/gpt-4oanthropic/claude-sonnet-4.5google/gemini-2.0-flash-exp
Bifrost handles API differences, authentication, and response formatting. This means you can offer users access to 10+ models without configuring 10+ API keys in LibreChat.
MCP Tools Integration
Models accessed through Bifrost automatically gain access to MCP (Model Context Protocol) tools configured in your Bifrost instance. When a user sends a message:
- LibreChat forwards the request to Bifrost
- Bifrost injects configured MCP tools into the request
- The model can invoke tools (file operations, web search, database queries, etc.)
- Bifrost executes tool calls and returns results
- The model incorporates tool results into its response
- LibreChat displays the final response to the user
This happens transparently - LibreChat sees standard tool calls in OpenAI format, regardless of the actual provider being used.
Model Discovery with fetch: true
Setting models.fetch: true enables dynamic model discovery. LibreChat queries Bifrost's /v1/models endpoint, which returns all available models across configured providers. This eliminates manual model list maintenance - add a new provider in Bifrost, and it automatically appears in LibreChat.
The endpoint returns models in OpenAI's format:
Bifrost translates models from all providers into this format.
Observability and Monitoring
All conversations through LibreChat are logged in Bifrost's dashboard at http://localhost:8080/logs. This provides:
- Request/Response Inspection: See exact messages sent between LibreChat and models
- Token Usage Tracking: Monitor consumption per conversation and per model
- Latency Metrics: Identify slow requests or provider issues
- Error Tracking: Debug failed requests with full error details
- Usage Patterns: Analyze which models users prefer, conversation lengths, etc.
This visibility is crucial for multi-user deployments where understanding usage patterns helps optimize costs and performance.
Load Balancing and Failover
Bifrost's load balancing distributes requests across multiple API keys or regions for the same provider. If one key hits rate limits or a region experiences downtime, Bifrost automatically retries with another. This improves reliability for LibreChat users:
- Reduced rate limit errors
- Better availability during provider issues
- Transparent failover without user awareness
Security Considerations
API Key Storage: The apiKey in librechat.yaml is visible to anyone with file access. In production:
- Use environment variables for sensitive values
- Restrict file permissions on
librechat.yaml - Consider using secrets management (Vault, Docker secrets)
Network Exposure: If Bifrost's port (8080) is exposed publicly, anyone can access your configured models. Options:
- Bind Bifrost to localhost only:
--bind 127.0.0.1:8080 - Use Docker networks to isolate services
- Enable Bifrost authentication and configure strong API keys
User Data: All conversations flow through Bifrost. Ensure compliance with data handling requirements if processing sensitive information.
Troubleshooting
LibreChat Can't Connect to Bifrost
Symptoms: "Failed to fetch models" or timeout errors
Solutions:
- Verify Bifrost is running:
curl http://localhost:8080/health - Check
baseURLmatches your network setup - For Docker, confirm
host.docker.internalresolves:docker exec librechat ping host.docker.internal - Check Docker networks if using container-to-container communication
Models Don't Appear in Dropdown
Symptoms: Empty model list or only default models shown
Solutions:
- Confirm
fetch: trueis set inlibrechat.yaml - Test Bifrost's models endpoint:
curl http://localhost:8080/v1/models - Verify providers are configured correctly in Bifrost
- Check Bifrost logs for errors when LibreChat queries models
Requests Fail with Provider Errors
Symptoms: "Invalid API key" or provider-specific errors
Solutions:
- Verify provider API keys are correctly configured in Bifrost
- Check Bifrost logs for detailed error messages
- Confirm the model string matches Bifrost's configuration (e.g.,
openai/gpt-4onotgpt-4o) - Test the provider directly through Bifrost's API to isolate issues
Docker Compose Override Not Loading
Symptoms: Changes to librechat.yaml don't take effect
Solutions:
- Verify
docker-compose.override.ymlexists in the same directory asdocker-compose.yml - Confirm volume mount syntax is correct
- Restart containers:
docker-compose down && docker-compose up -d - Check container logs:
docker-compose logs api
Conclusion
Integrating LibreChat with Bifrost transforms a single-application chat interface into a multi-provider AI platform. Users gain access to models from OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and others through a unified interface, while administrators benefit from centralized observability, load balancing, and tool integration. The configuration is straightforward - a single YAML file addition - and the benefits scale as you add more models, tools, and users to your deployment.
The architecture separates concerns effectively: LibreChat handles UI and conversation management, Bifrost handles provider abstraction and traffic management, and underlying model providers handle inference. This modularity makes it easy to swap components, add capabilities, or scale horizontally as usage grows.